Table of Contents
ToggleOrganizational Design
When delving into the realm of organizational design, one must understand its pivotal role in shaping the structure, processes, and culture of a company. It encompasses how various components within an organization interact and operate cohesively to achieve overarching goals. As I explore this topic further, I aim to shed light on the significance of strategic organizational design in today’s dynamic business landscape.
In essence, organizational design serves as the blueprint that dictates how tasks are divided, communication flows, and decision-making processes unfold within a company. It is not merely about arranging boxes on an organizational chart but rather about creating an environment where efficiency, innovation, and collaboration thrive. Through my analysis, I hope to uncover how effective organizational design can drive performance and foster adaptability in an ever-evolving market.
As we navigate through the intricacies of organizational design, we’ll delve into various models, approaches, and best practices that companies employ to enhance their operational effectiveness. By examining real-world examples and case studies, we can glean insights into how successful organizations strategically craft their structures to stay agile and competitive amidst changing industry landscapes.
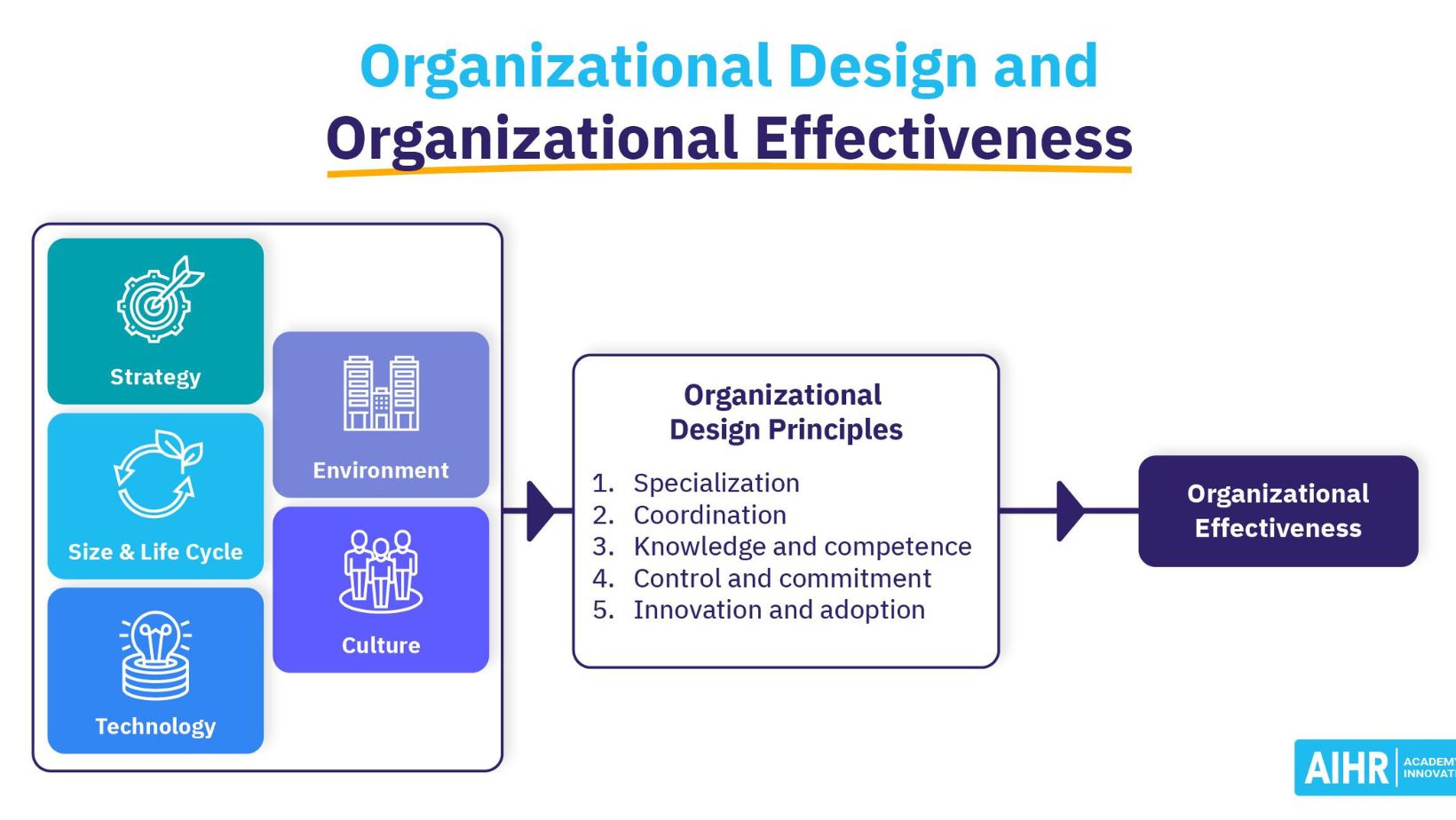
The Importance of Organizational Design
When it comes to ORGANIZATIONAL DESIGN, it serves as the blueprint that shapes how a company operates. It is not just about the structure; it influences everything from communication channels to decision-making processes. Think of it as the ARCHITECTURE that determines how all the pieces fit together in a business puzzle.
One key aspect of organizational design is its impact on EFFICIENCY and PRODUCTIVITY. A well-designed organization streamlines workflows, reduces redundancies, and ensures that resources are utilized effectively. This can lead to cost savings and improved output, ultimately contributing to the bottom line.
Moreover, organizational design plays a crucial role in EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT and SATISFACTION. When employees understand their roles within a clear structure, feel empowered to make decisions within their authority, and see opportunities for growth, they are more likely to be motivated and committed to their work.
Another vital point is how organizational design can foster INNOVATION and ADAPTABILITY. Companies that have flexible structures are better equipped to respond to market changes, embrace new technologies, and stay ahead of competitors. By encouraging creativity and cross-departmental collaboration, organizations can drive continuous improvement.
In essence, organizational design sets the stage for success by aligning strategy with execution, promoting accountability at all levels, and creating an environment where individuals can thrive professionally. It’s not just about how an organization looks on paper; it’s about how well it functions in practice—driving results through intentional design choices.
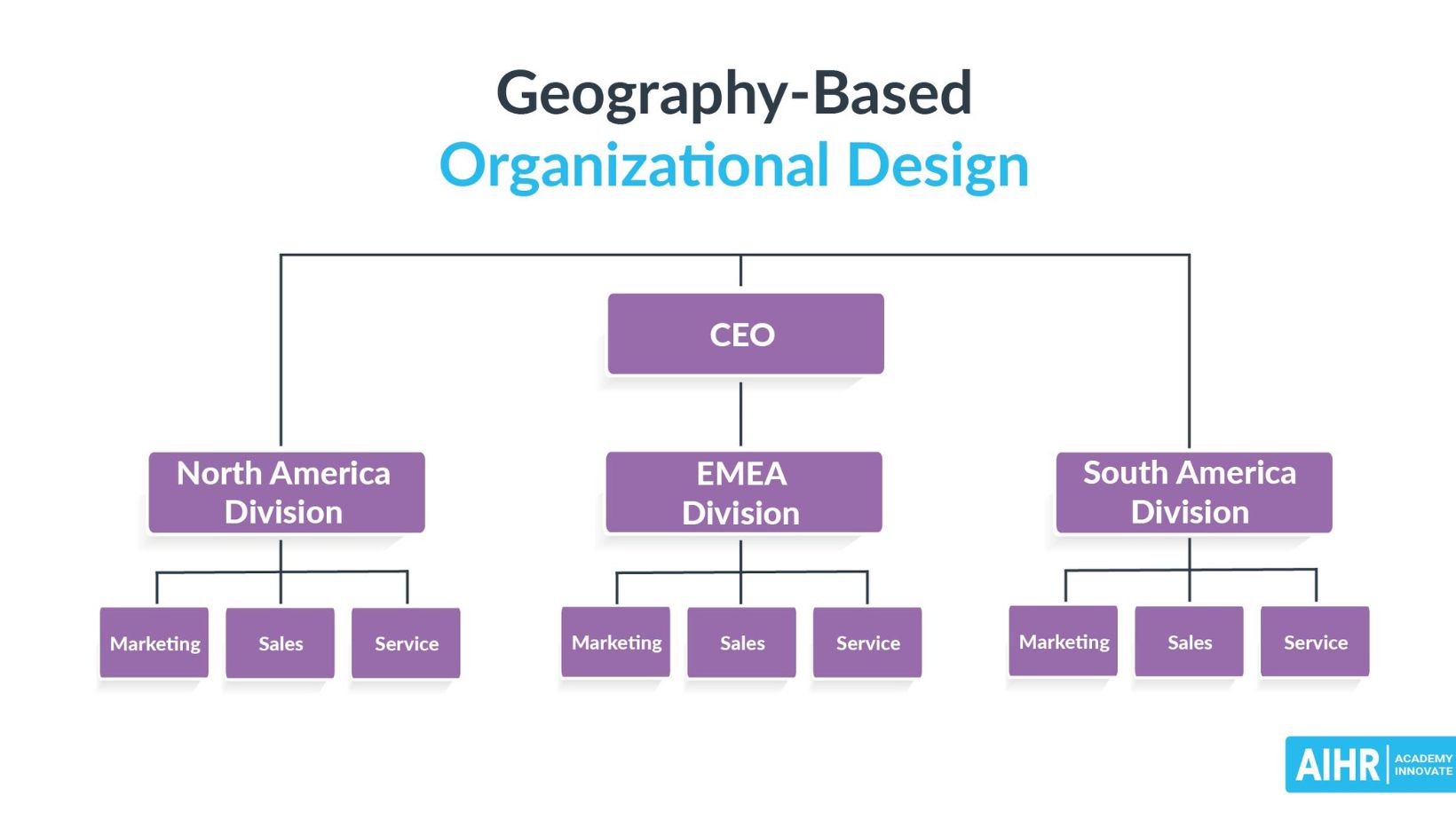
Key Elements of Organizational Design
When delving into the realm of organizational design, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamental components that shape and define how a company operates. These key elements serve as the building blocks upon which efficient structures are erected, enabling businesses to function optimally and adapt to changing environments seamlessly.
1. Structure
The structural framework of an organization is akin to its skeletal system, providing support and defining relationships between various roles within the company. Whether it be hierarchical, flat, matrix, or network-based, the chosen structure influences communication flows, decision-making processes, and overall efficiency. For instance:
- Hierarchical Structure: Traditional top-down approach with clear lines of authority.
- Flat Structure: Fewer tiers of management promoting quick decision-making.
- Matrix Structure: Cross-functional teams enhancing collaboration across departments.
2. Culture
Organizational culture embodies the shared values, beliefs, and behaviors that characterize a company’s identity. Cultivating a positive culture fosters employee engagement, boosts morale, and ultimately drives productivity. Examples include:
- Innovative Culture: Encourages creativity and risk-taking.
- Customer-Centric Culture: Focuses on exceeding customer expectations.
- Collaborative Culture: Emphasizes teamwork and open communication.
3. Processes
Efficient processes are vital for streamlining operations and ensuring consistency in performance standards. From workflow automation to quality control measures, well-defined processes enhance productivity while minimizing errors or delays. Consider implementing:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) for repetitive tasks.
- Continuous improvement initiatives like Lean or Six Sigma methodologies.
- Technology integration for seamless data management and analysis.
Understanding these key elements empowers organizations to design structures that align with their strategic objectives while fostering an environment conducive to growth and innovation. By leveraging structure, culture, and processes effectively, companies can navigate complexities with agility while maintaining a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business landscape.